On this page
In Sweet for ArcGIS you can define the spatial relationship of one feature to another feature either in the same layer or across multiple layers in a web map. Sweet for ArcGIS will enforce these spatial rules to ensure your data is always valid when being created and edited.
What type of rules are available?
Spatial relationship rules provide a powerful means of validating data at the point of collection. This enforces high data quality in your datasets. There are a number of geospatial rules you can set up for your data in Sweet for ArcGIS.
- Single Layer rules apply to the spatial relationship of features within a single layer to other features and themselves. For example, a line feature may be prevented from overlapping itself and other features that exist within the same layer.
- Multi Layer rules apply to the spatial relationships between features that exist in different layers within a web map. For example, a point feature added or edited on the map may only be valid if it is contained within a specific type of polygon.
To allow spatial relationship rules to be configured based on the different subtypes of a layer, you need to turn on the Topology Rules per Sub type option in the Data panel of the Data Rules Editor.
Single layer rules
To add rules which apply to features in the same layer you need to follow these steps:
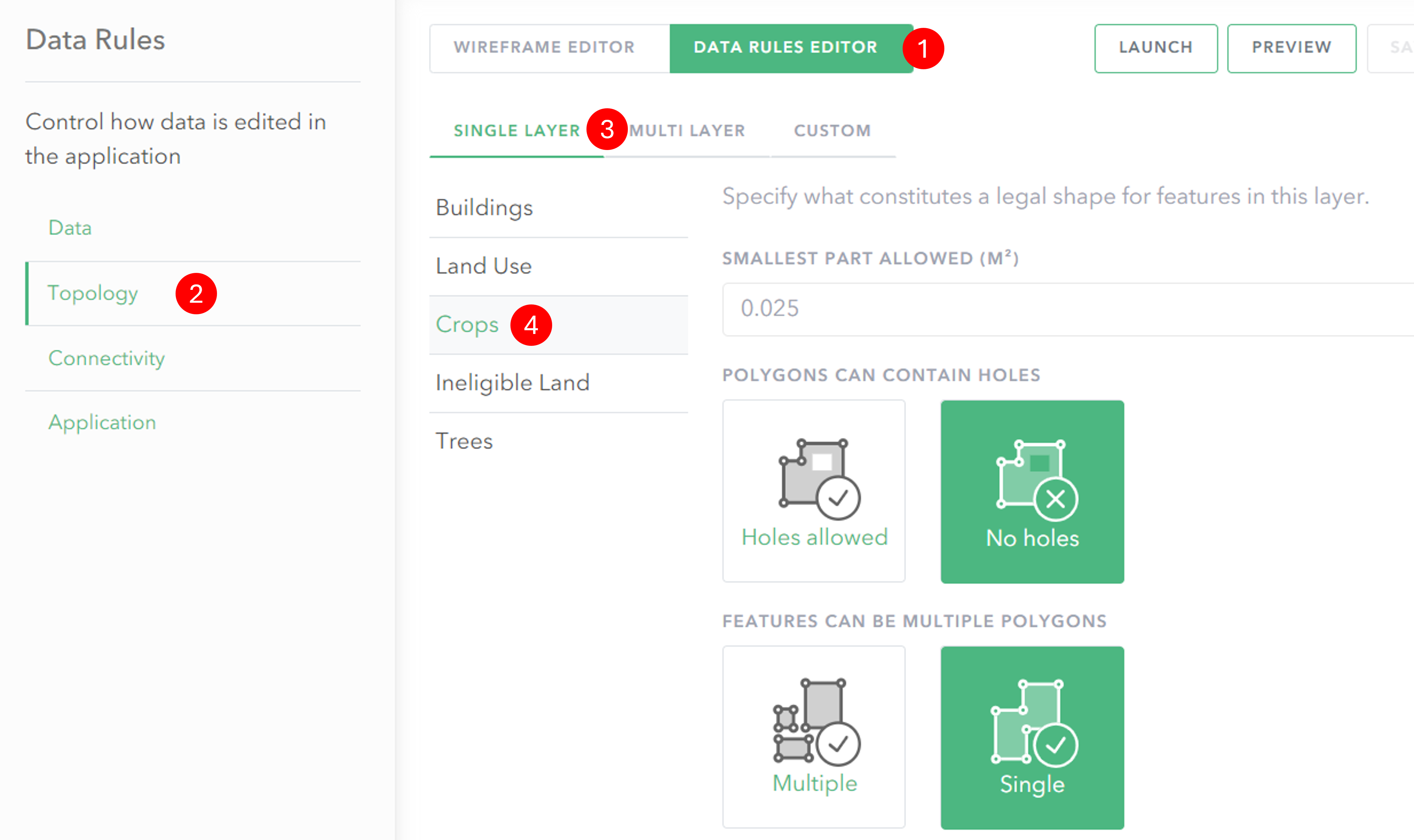
- Click on Data Rules Editor to switch to the rules view.
- In the Data Rules menu click Topology to switch to the spatial rules editor.
- Click on the Single layer tab.
- Click on the layer you want to add a rule to and then configure the rules that will be applied during feature creation and editing.
Single layer – options
Smallest part allowed
This rule applies to line and polygon features. It allows you to determine the smallest size a feature can be to be considered valid.
Multipart features
Features which are multipart allow you to capture multiple features which have the same properties including Object and Global ID. Otherwise each feature must be single part.
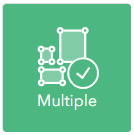
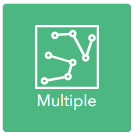
Overlaps
You can define whether features in the same layer are allowed to overlap. For line features you can choose whether to allow or prevent overlaps with itself and/or other features within the same layer.


Holes – (polygons only)
You can define whether a polygon feature is allowed to contain holes.

Cross and touch – (lines only)
Cross and touch can only be applied to line features. You can choose whether to allow them or prevent them for either the same feature or for other features in the same layer.


Multi layer rules
To add rules which apply to features in multiple layers you need to follow these steps:
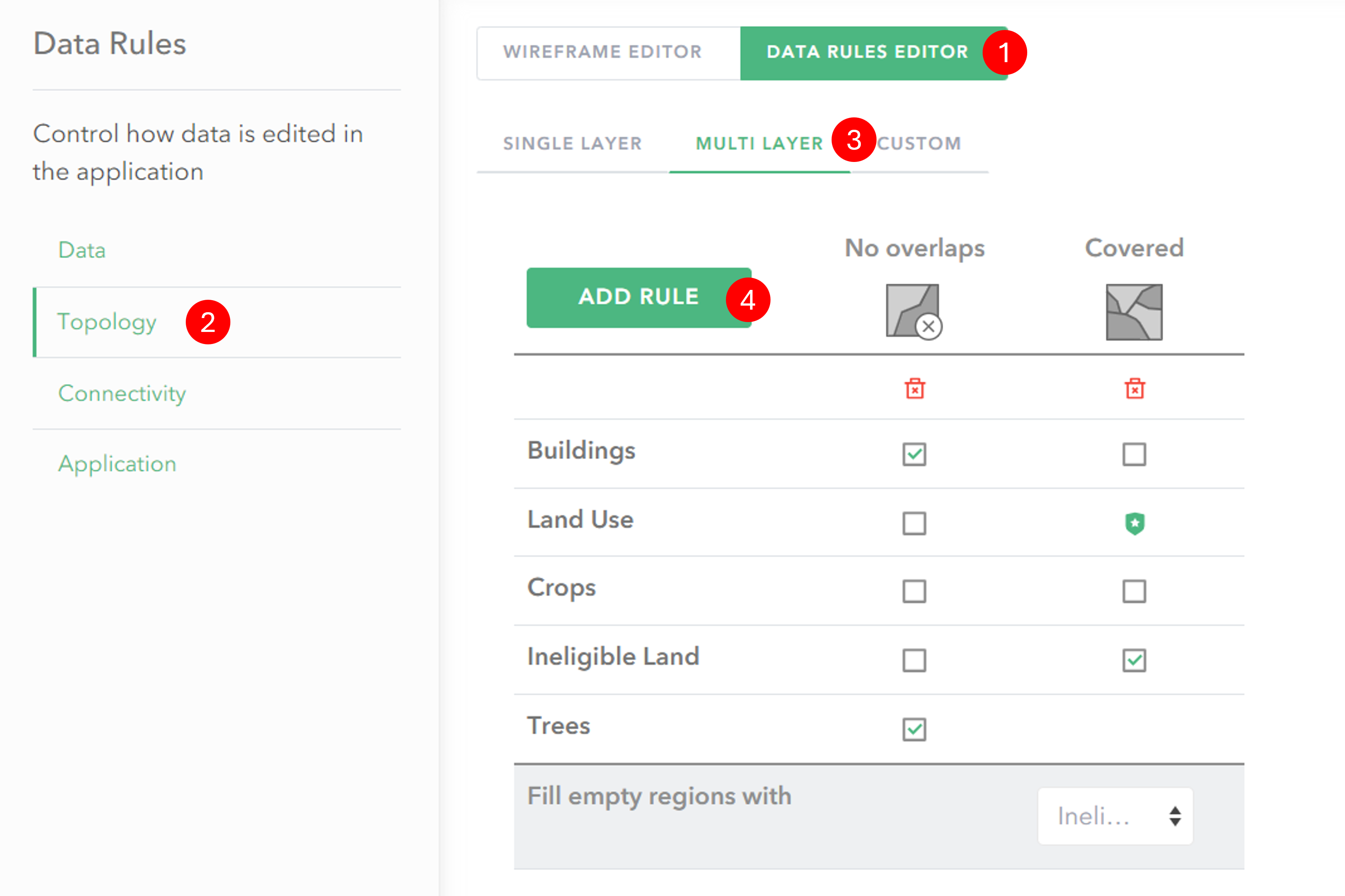
- Click on Data Rules Editor to switch to the rules view.
- In the Data Rules menu click Topology to switch to the spatial rules editor.
- Click on the Multi layer tab.
- Click on the Add Rule button and select a rule type.
- Configure the rules for each layer by ticking the relevant checkboxes.
Multi layer – options
No overlaps
You can define whether or not features in different layers are allowed to overlap.

Contained
Contained requires at least one polygon feature service in your web map which will act as the containment feature. You can then define what features must be contained within your polygon features.

Covered (polygons only)
With this rule polygons in the parent layer must be completely covered by polygon features from one or more other layers. The features must form a single surface covering the polygon with no gaps between features.
This rule can be used to ensure complete coverage of an area, with no gaps. In the options for the rule you can select what type of feature defined in the layer feature template should fill any empty areas.
An example application of this rule is for land classification. An area of land drawn as a polygon may be given a broad classification of development which then contains sub-categories of a specific development type (e.g. commercial, road, housing etc.). The covered rule could be used to automatically fill any uncategorised area within the development with polygons representing undesignated land-use.

No line intersects (lines only)
With this rule set lines will not be allowed to intersect with other line features of other layers defined in the rule.
No line touch (lines only)
With this rule set lines will not be allowed to touch other line features of other layers defined in the rule.
Related
With this rule you can set layers to be related to one another topologically. This means that they will share, crack and cluster their vertices together.

